AFFILIATE MARKETING WITH GOOGLE ADS
The Ultimate Guide On How To Scale Up Your Affiliate Marketing Performance With Google Ads
Learn step-by-step how to set up your affiliate marketing campaigns and uncover best practices for analyzing conversion data. Integrate your conversion data into Google Ads campaigns and maximize your ROI.
1. How To Set Up Affiliate Conversion Tracking In Google Ads
Before you start setting up any Google Ads campaigns, you need to think about what you would like to accomplish with them. Do you want people to interact with your content? Do you want them to sign up for a newsletter? Do you want someone to click on an affiliate link, or do you actually want someone to buy a product? Now, you can have multiple goals that you would like to accomplish with your campaigns, but you must define each one of them first and create a small overview for yourself.
Now, a very simple overview of conversions for an affiliate publisher could look like this:
- The user clicked on the affiliate link leading to the merchant
- The user generated a sale on the merchant’s website
Many affiliate publishers have the misconception that it is impossible to track conversions on the merchant’s website in Google Ads without placing a pixel on their website. Still, it is quite easy once you understand the data flow. You need to consider that advertisers have already placed a pixel or code of the affiliate network on their website to trigger conversion events. Now, you can use that to help you track conversions properly by using the affiliate networks’ API, Postback URL, and SubIDs.
You might think this is getting too technical already, but we will spear you with the technical aspects since wecantrack provides a JavaScript tag and WordPress plugin that will handle them for you (you can find more information on how to make use of those here). But this is the process put in simple words:
The idea is to track sessions and clicks from your website and place unique click IDs in the SubID parameters of your affiliate links. The conversions are then collected via APIs or Postback. The SubID values will help attribute the conversions to the sessions, delivering the information needed to integrate the conversion data in tools like Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook, and more.
The following two dataflow charts demonstrate the dataflow of an affiliate publisher that does not use data attribution and an affiliate publisher that does attribute and integrate via wecantrack.
Data Flow Without Conversion Attribution
Data Flow With Conversion Attribution Via wecantrack
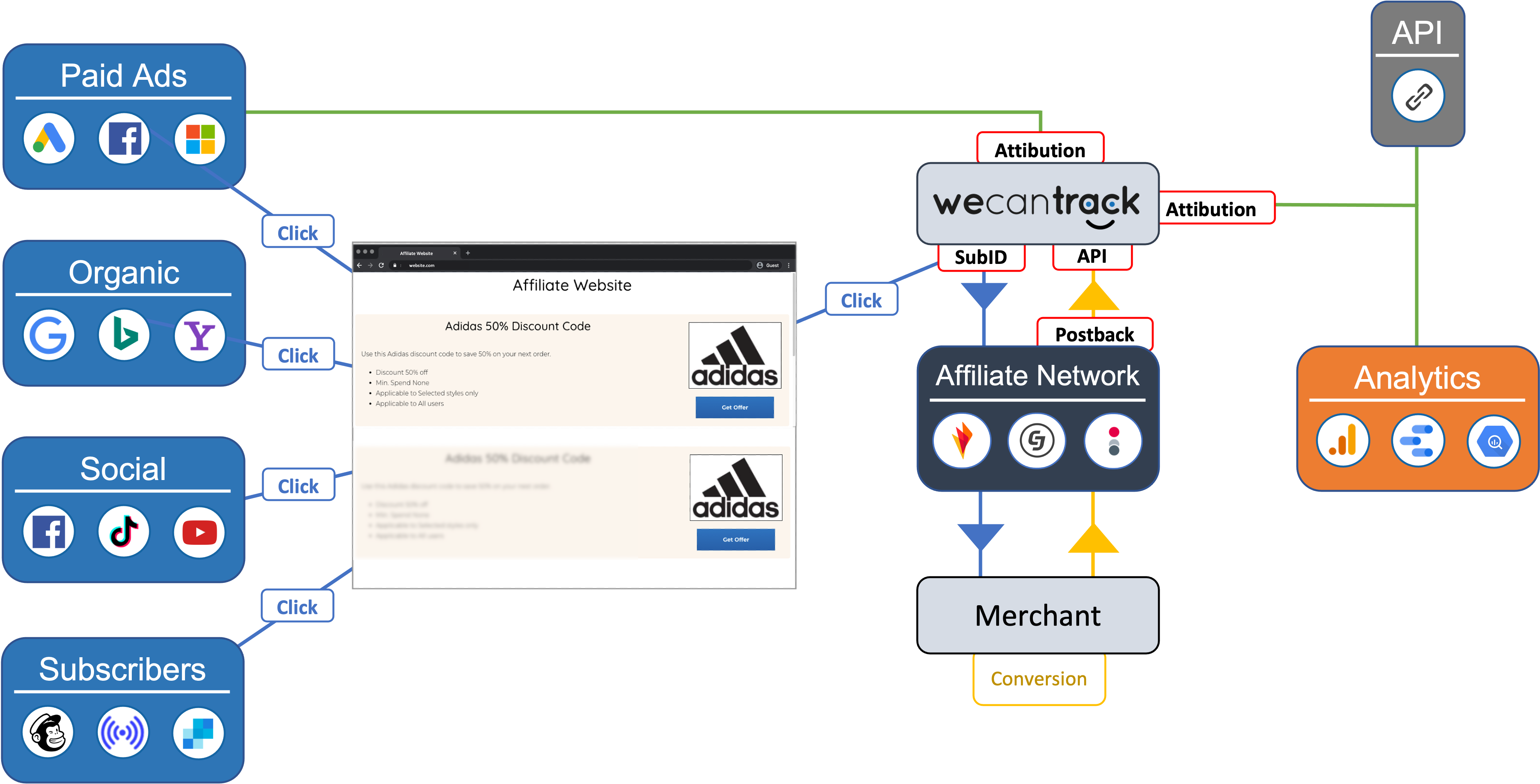
- place unique click IDs in the SubID parameters of your affiliate links
- collect conversions via APIs or Postback
- attribute the conversions to the clicks and sessions with the help of the SubID values
Once your conversion data is attributed to your traffic data, it can be imported into Google Analytics as ecommerce conversion events, which are also available as a goal. After linking your Google Analytics and Google Ads accounts, you can then automatically import conversion data registered in Google Analytics in Google Ads.
It is also possible to integrate affiliate conversion data directly in Google Ads without using Google Analytics. If you want to integrate your conversions directly or via Google Analytics, follow our Google Ads Integration guide.
If you create click goals, you can also import them into Google Ads. We advise setting them as secondary conversion actions, though, as they will only be placed in All Conversions. You can then set up a custom column to use the click goal as a metric.
This way, you will have a new column available, which will show the number of clickouts your campaigns generated, which you can place next to your conversion column.
Click here to see a step by step guide on how to create a Clickout column within Google Ads.
2. How To Create Relevant (Affiliate) Website Audiences For Google Ads With Google Analytics 4
We placed audience creation as the second topic, even before campaign creation, because the sooner you set up your audiences, the sooner you will be able to use them.
Audiences take time to grow, and they need to contain enough users for you to use them in your campaigns. So, after setting up your conversion tracking, this should be the first thing you do.
We will explain to you how exactly you can set up these 3 essential audiences:
- Users who clicked on an affiliate link but did not generate a sale
- Users who generated a sale
- Users who did not generate a sale
Of course, you can narrow down the audiences further by adding more conditions, such as a landing page, page, or exit page.
How To Set Up An Audience In Google Analytics 4
Here is an example of how to set up the audience ‘Users who clicked on an affiliate link but did not generate a sale’:
- Go to Admin > Audiences (Under Property) > Audiences
- Click on ‘+ NEW AUDIENCE’
- Click on ‘Create Custom Audience’
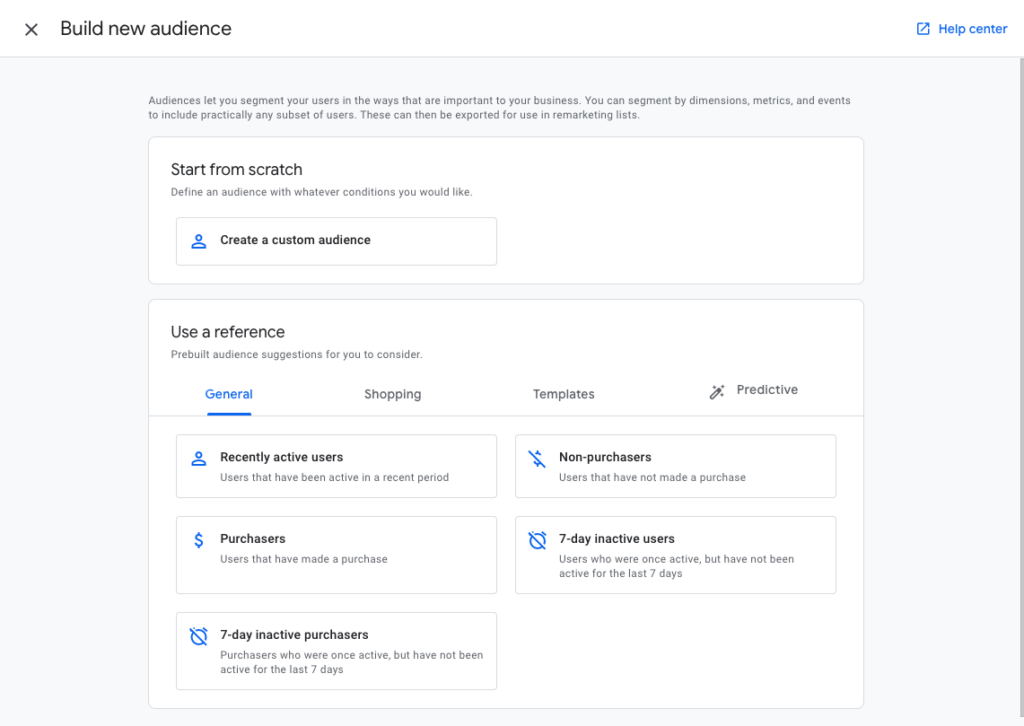
- Give your new audience a name
- In 'Include users when' select 'add new conditions' > 'Events' > 'wct_click'
- Click 'Add group to exclude'
- Click 'Add new condition' > 'Events' > 'wct_conversion'
- In 'additional audience settings' set the membership duration to 'set to maximum limit'
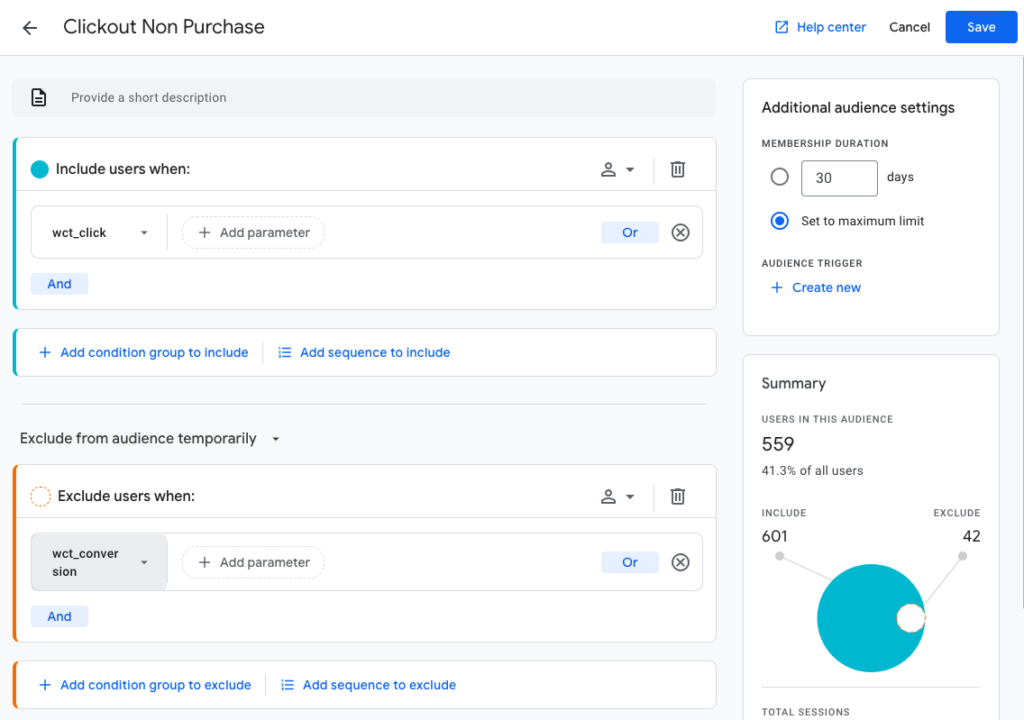
Visitors Who Clicked On An Affiliate Link But Did Not Generate A Sale:
Include users when:
Event > wct_click
AND
Exclude users when:
Event > wct_conversion
Visitors Who Generated A Sale:
Include users when: Event > wct_conversion
All Visitors Who Did Not Generate A Sale:
Include users when: Event > Session Start
Exclude users when: Event > wct_purchase
3. How To Set Up (Affiliate) Marketing Campaigns In Google Ads
Now that you have set up conversion tracking and created your first audiences, we can dive into the campaign creation within Google Ads.
Google Ads offers multiple ways to create campaigns:
- Via their user interface
- Via the Google Ads Editor
- Via CSV imports
- Via API
Creating campaigns via the user interface takes the longest but is also the simplest approach for beginners.
Using the Google Ads Editor, you can more easily copy & paste campaigns, ad groups, keywords, and ads. It also allows you to make many quick adjustments at once easily. You should be a little experienced with Google Ads before using the Google Ads Editor.
The CSV import functionality is by far our favorite way to create campaigns. When you know your way with Excel or Google Sheets, you can create hundreds of campaigns with thousands of keywords within just one hour! (Are you interested in learning more about this? Let us know, and we might set up a webinar about it.)
3.1 How To Structure A Google Ad Search Campaign
Before you build your first campaign, you should consider what kind of campaign you want to create and how you want to structure it. Google Ads offers Search, Display, Shopping, Video, Smart, and Discovery campaigns. We will focus on search campaigns since they are the most basic Google Ads campaign type, which, in many cases, also performs best.
In Google Ads, a campaign consists of ad groups, keywords, and ads. The following graphic visualizes this:
Campaign

3.1.1 How Many Keywords Should I Use In An Ad Group?
Now, how many keywords should be placed within an ad group is up to the person creating the campaign. It depends on structural preferences, but having too many different keywords in just one ad group can be limiting. We always recommend starting with only a few keywords per ad group and creating more ad groups. This approach will later on give you more control since you have more capabilities on the ad group level than on the keyword level. In general, the keywords within one ad group should be very similar. We often just place one or two keywords within one Ad Group.
If you decide to use multiple different keywords within one ad group, that is of course totally fine. But if at one point certain keywords perform very well, it is best to set up a separate ad group for each well performing keyword.
3.1.2 How Many Ads Should I Use In An Ad Group?
Regarding ads, it is easier to give a number. Google recommends to place three ads in search campaigns. Two text ads and one responsive search ad.
3.2 What Are Match Types In Google Ads And Which One Should I Use?
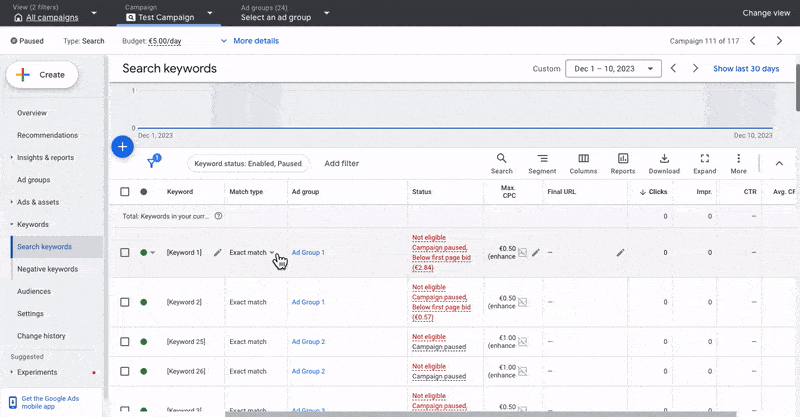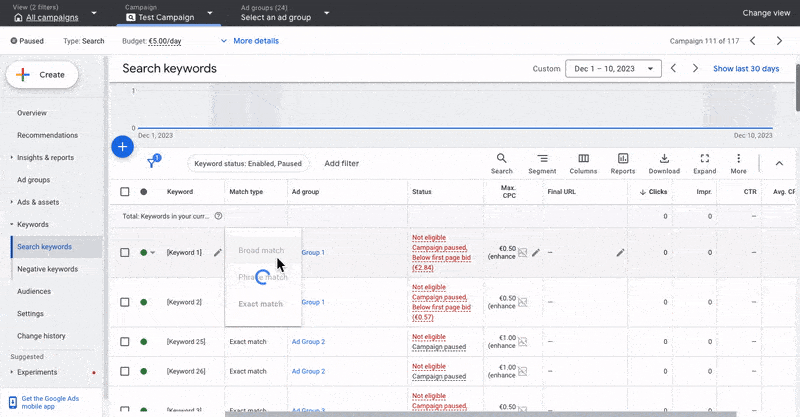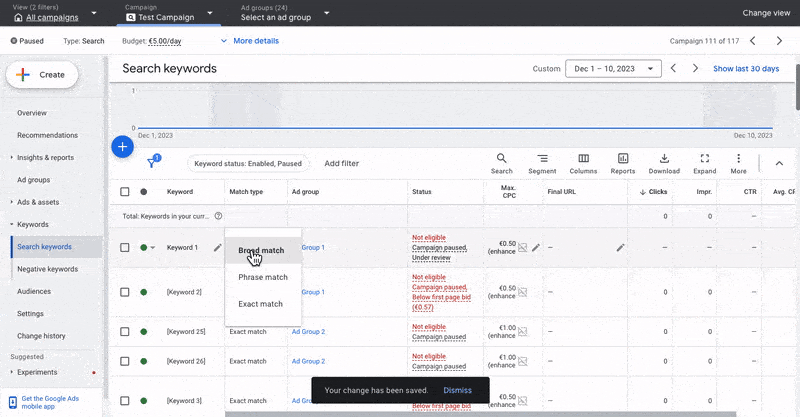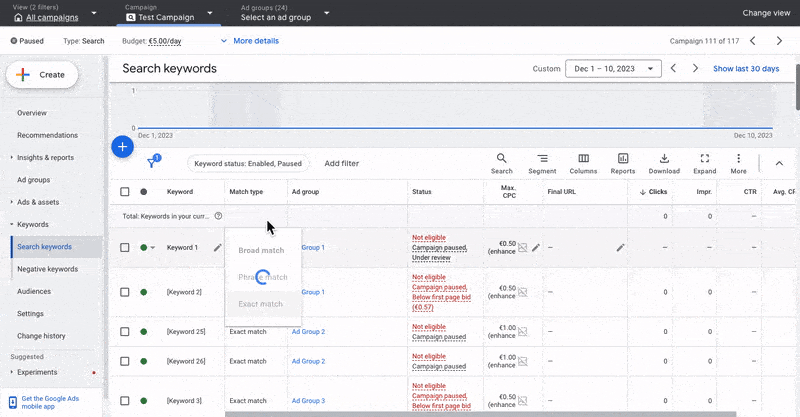
When you set up your keywords, you must set match types. There are three match types available in Google Ads: broad, phrase, and exact.
Broad Match Type
Broad keywords will trigger impressions when people search for keywords that Google associates as similar to the keyword you provided. This match type is great for generating a lot of impressions and clicks to gather some data. However, regarding conversion rates, this match type usually does not perform well if you do not narrow the audience further.
Phrase Match Type
Phrase keywords will trigger impressions for users who include your keyword in their search query. So, this match type is more specific than broad. While it will generate fewer impressions and clicks than broad, these impressions and clicks will be more relevant and will most likely perform better in terms of conversion or interaction rates.
Exact Match Type
Exact keywords will trigger impressions when users type in exactly what you defined as the keyword. With this match type, you will gain the most control, and you can be very specific about which terms your ads will be triggered.
You will generate fewer impressions with an exact match keyword, but the relevancy can be enormous, leading to higher conversion or interaction rates. If you use exact match keywords, you will need to add many keywords to your campaigns in order to generate a lot of traffic.
In general, the more specific your campaigns are, the more conversion-oriented they are. But to get there, you will need to start broader since you will need data to know which keywords perform well and which don’t.
We suggest you start with phrase—or exact-match keywords and use broad-match only if you want to find new keyword terms, unless you have narrowed down your audience and are certain you are targeting users who are interested in your services or products.
3.3 How To Find The Right Keywords For Google Ads Campaigns
There are different ways to find the right keywords for your campaigns. we will focus on 5 approaches:
- Check your landing page and filter out the relevant keywords
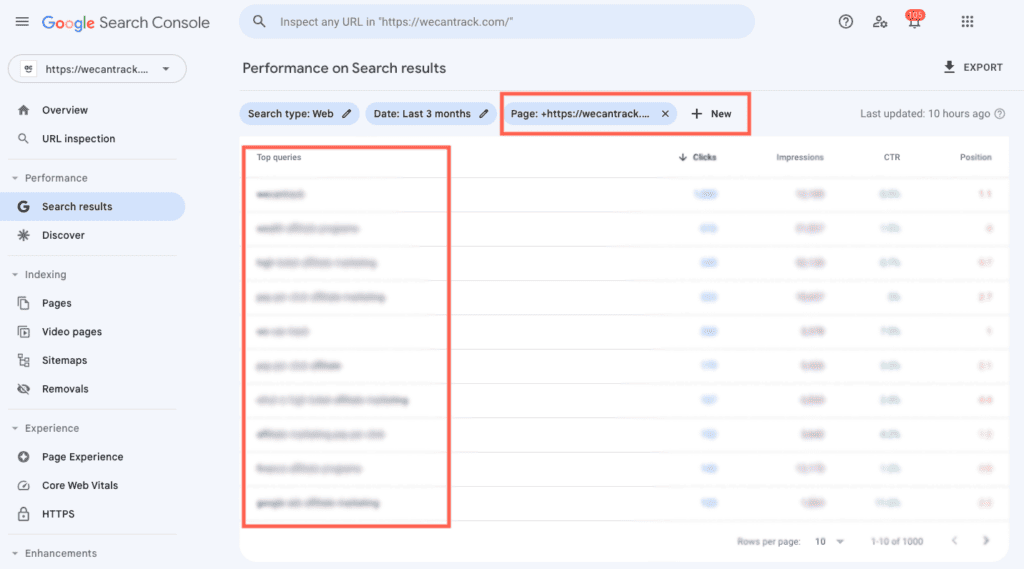
Simply go through your landing page and check which of the words you used are the most relevant to the readers. What would you search to end up on a page like this? - Take a look at Google Search Console to find out which keywords perform well organically
Go to Performance > Queries and filter on the landing page you want to promote. Now you will see many search queries that drove traffic to your website organically which you can also use within your campaigns.
- Do keyword research with tools like Google Ads Keyword Planner, Ubersuggest, Ahrefs, Semrush, Search Metrics, etc.
Since you already have a list of keywords, you can use the most significant ones to search for further alternatives and long-tail keywords that you can include in your campaigns. - Set up a broad-match AdGroup or Campaign
Using broad-match, Google will trigger impressions for search terms that fit the ones you provided. Use your most significant keywords for this method, give it an acceptable budget and low CPC bid, and monitor this closely to ensure you are not spending too much on this. Let this run until you have enough data to go through.
To find the search terms that triggered your ads, select the campaign / AdGroup, go to Keywords > Search terms, and select the metrics (columns) you would like to see. Now, you can analyze the search terms that were used and pick the ones that performed best in terms of clicks, CTR, or maybe even conversions. - You can go on Google and type in your most significant keywords in the search bar, Google will give you suggestions of long tail search queries which you can include in your campaigns.
3.4 Which Budgets & Bids Should I Use For My Google Ads Campaigns?
There are different approaches when it comes to budgets and bids. We usually use a careful approach where we would rather start with low bids and budgets and move our way up instead of starting high and moving down. However, you could miss out on some keyword opportunities with this approach. The starting high moving down approach will deliver much more data to you but also cost you a lot more money.
To determine an initial bid, we look at Google Ads’ Keyword Planner, which gives us an indication of what top-of-page bids are being used.
Example:
Let’s say we want to promote a Lenovo Thinkpad offer. we are allowed to use the term “Thinkpad” for SEA but not the brand keyword “Lenovo.” we can then check in the keyword planner what range of CPCs are being used for “Thinkpad” related search terms.
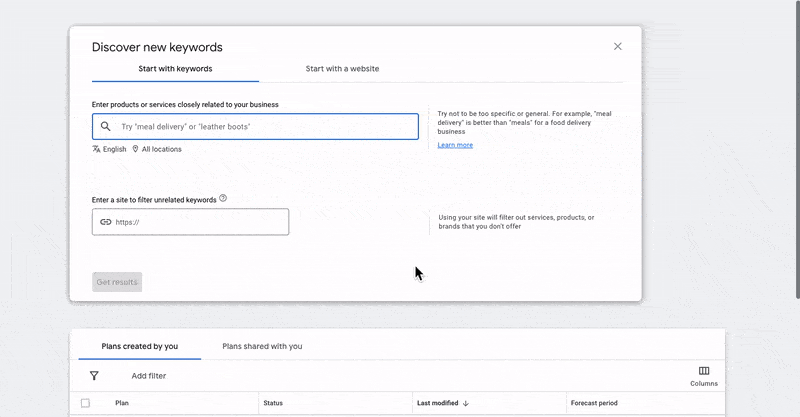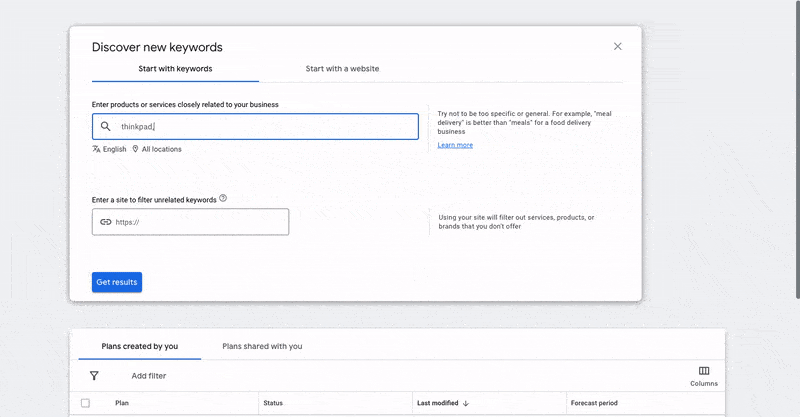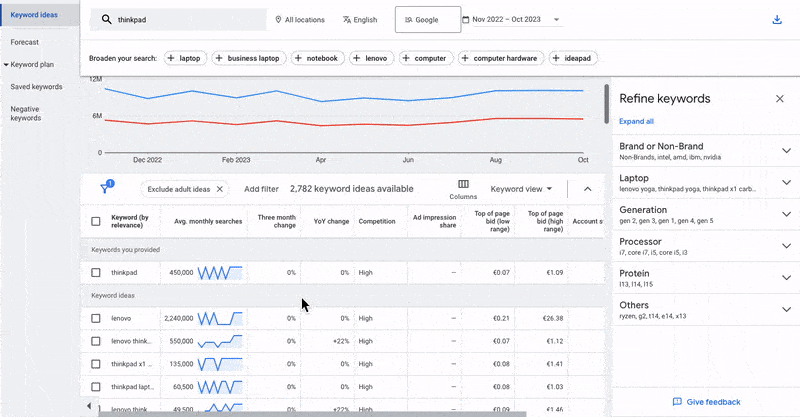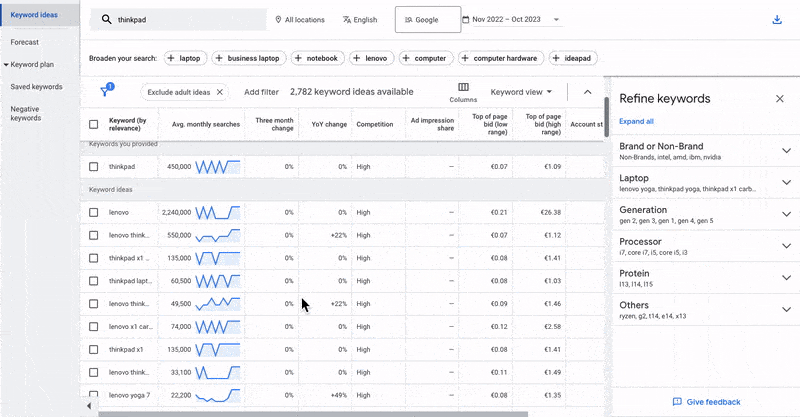
We would set up 2 different ad groups for the listed keywords.
1. Ad Group for the keyword “ThinkPad” with a bid of 10 cents on an ad group level.
2. Ad Group for the keywords that contain “ThinkPad” with additional terms that define we have a special offer here with a bid of 30 cents on an ad group level.
As a daily budget, we would use 5 to 10 Euros for this campaign.
Now, after one day, we would check how those settings performed and adjust the bids on the keyword level to reach a satisfactory number of impressions for a reasonable price. we will continuously do so and, at one point, start optimizing our bids based on actual conversion data, which we will explain in the optimization chapter.
Once you gather enough data, you can also automate the bid adjustments using Target ROAS or Target CPA. You will also find more information about that in the optimization chapter.
3.5 How To Make Use Of Audiences In Google Ads And Set Up Retargeting Campaigns
Remember the audiences you created before? Well, now it is time to put them to use.
You can set up pretty broad campaigns or display campaigns and narrow down the visitors you target by setting up target audiences or excluding certain audiences.
3.5.1. The First Thing We Would Do For Broad Search And For Display Campaigns Is Exclude Converters:
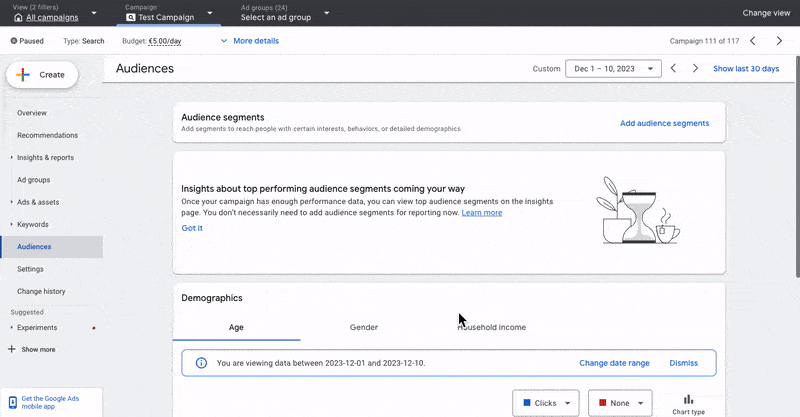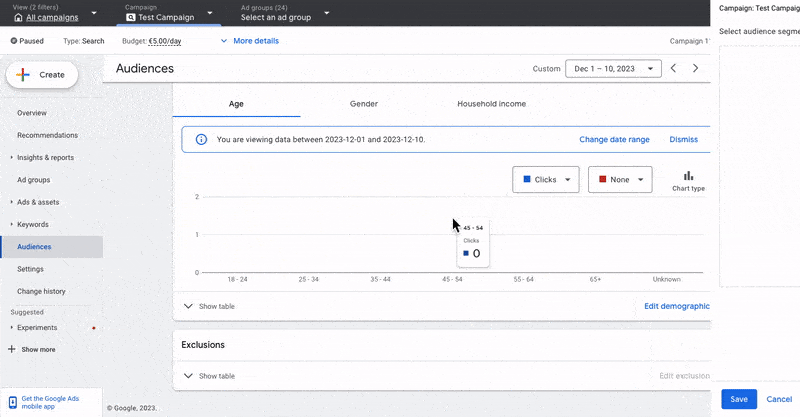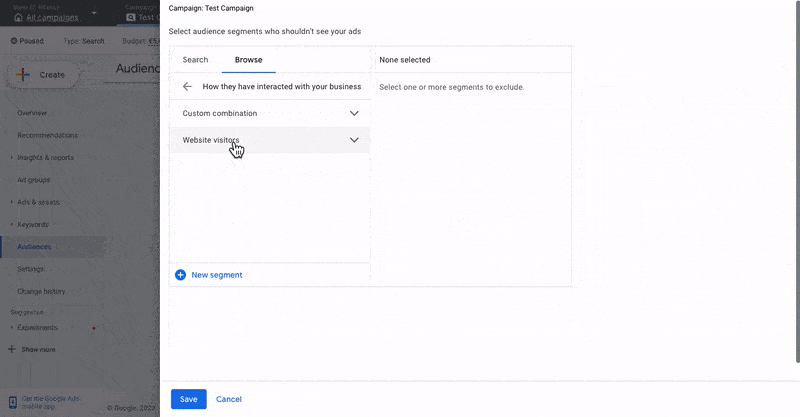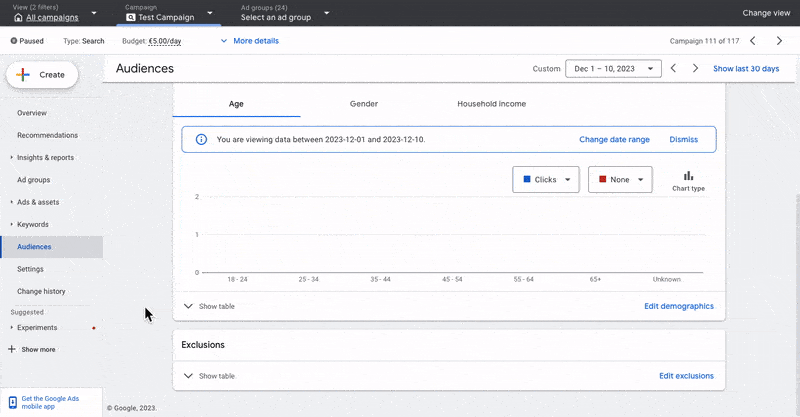
- Select the campaign you want to narrow down
- Click on Audiences > Exclusions
- Click on the + button > Exclude audiences
- Go to Browse > How they have interacted with your business > Website visitors
- Select the converter audience you have created before
With this audience exclusion you can make sure you do not keep targeting users who already bought something. This is especially interesting for display campaigns since you sort of force your ads on people here. For search ads this exclusion is not really necessary (unless it is a very broad search ad) since the user still seems to be interested in the product / service / search term, else he or she would not be searching for it.
3.5.2. Another Audience We Would Use For Broad Search And For Display Campaigns Is Users Who Clicked But Did Not Convert:
- Select the campaign you want to narrow down
- Click on Audiences > Audiences
- Click on the + or edit button > Edit audiences
- Select an ad group
- Go to Browse > How they have interacted with your business > Website visitors
- Select the “clicked but did not convert” audience you have created before
With this audience, you will only target users who engage with the content on your website but abandon the funnel on the advertiser’s website. You can try to get these users to engage with your content again and maybe make them convert this way. Remember, over 50% of the conversions for many websites come from returning visitors.
3.5.3. You Can Also Create A Campaign Targeting Users Who Are Similar To Your Converters:
- Select the campaign you want to narrow down
- Click on Audiences > Audiences
- Click on the + or edit button > Edit audiences
- Select an ad group
- Go to Browse > How they have interacted with your business > Website visitors
- Select the “Similar to Converters” audience which was automatically created by Google
With this audience you will be able to target users who Google considers similar to your converters based on the user data they collected.
3.6 How To Make Use Of Ad Placements In Google Ads
You can adjust where your ads should be placed for display campaigns. If your competitors have display ads showing on their websites, you can take advantage of that opportunity and create display campaigns that will show on your competitors’ websites.
Do some research and identify which of your competitors’ websites use display ads. Once you have a list of websites, you can go to ‘Placements’ within your display campaign and click on Edit Placements. Select the relevant ad group, then select ‘Targeting’ and go to ‘Websites’. Click on ‘Enter multiple placements’ and fill in the websites that you have collected.
After saving the placement adjustments, your campaign will only place display campaigns on the defined websites.
3.7 How To Leverage Campaign Assets In Google Ads
One important aspect often overlooked by publishers when setting up your campaign involves using a variety of ad assets, formerly extensions, to amplify your ad’s performance. These assets are powerful tools that can notably enhance your Click-Through Rate (CTR) and elevate your overall campaign optimization score. Google Ads offers an array of ad assets, each designed to serve a specific purpose and engage your audience in different ways:
- Sitelink Extensions: Direct users to specific pages on your site, giving them more options to explore and engage with your offerings.
- Callout Extensions: Highlight unique selling points, special offers, or key benefits to attract attention and encourage clicks.
- Structured Snippets: Showcase specific aspects of your products or services, such as types, models, or features, to provide additional context to potential customers.
- Call Extensions: Add a clickable phone number to your ad to enable users to call your business directly, facilitating immediate connections.
- Location Extensions: Display your business’s physical location alongside your ad, making it easier for local customers to find and visit your establishment.
Integrating these diverse ad assets strategically into your Google Ads campaign can yield significant benefits like:
- Improved Click-Through Rate (CTR): By providing more information and engaging elements within your ads, you increase the likelihood of users clicking through to your website.
- Enhanced Relevance and Visibility: Utilizing extensions adds more context to your ad, making it more relevant to users’ queries and increasing its visibility in search results.
- Higher Optimization Score: Leveraging these assets positively impacts your campaign’s overall optimization score, indicating improved ad quality and relevance.
4. How To Monitor Google Ads Affiliate Campaign Performance
You can use different platforms to monitor your Google Ads campaign performance. We personally prefer to monitor campaign performance within Google Ads itself since it allows us to take action based on the data quickly.
Other platforms you can use to monitor your performance are:
- Google Analytics
- wecantrack dashboard
- Looker Studio
- Google Sheets
Monitoring Campaign Performance In Google Ads
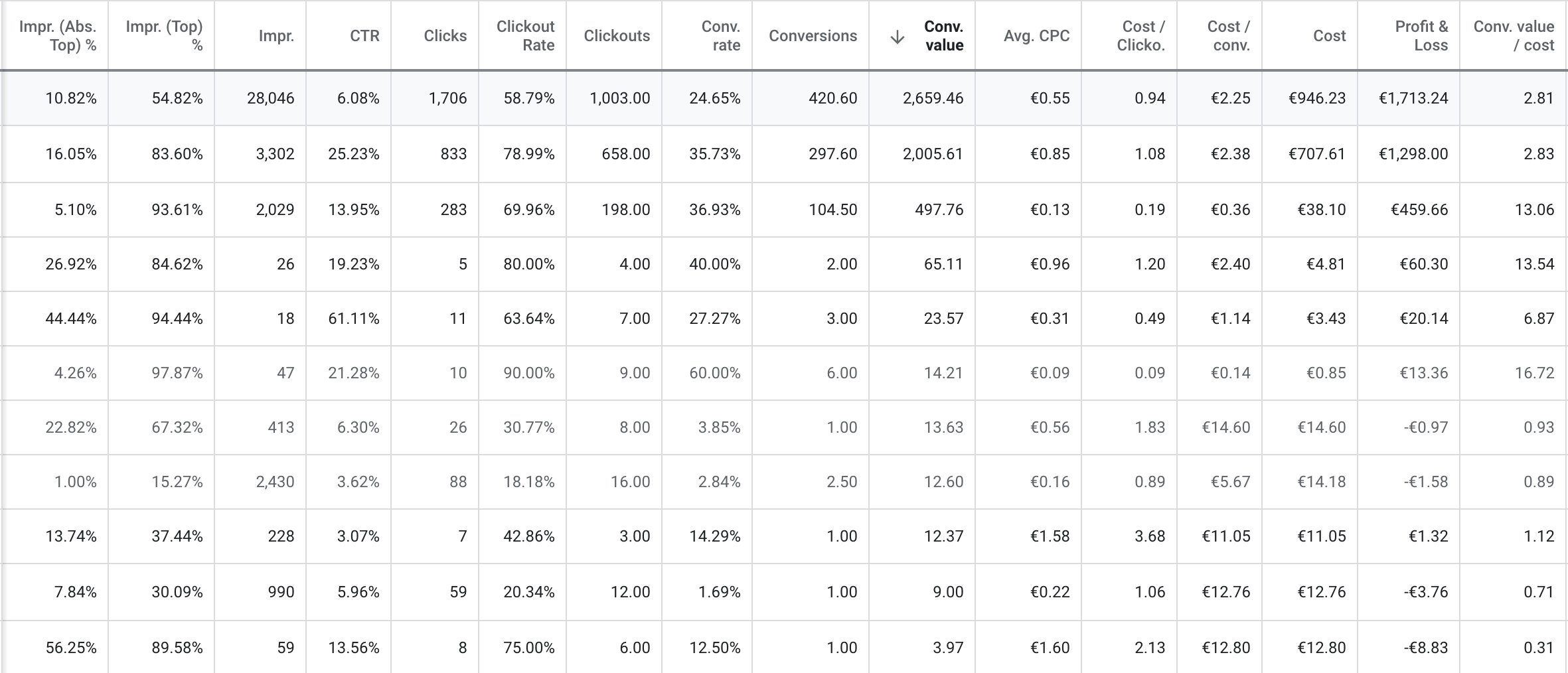
When you have fully integrated your conversion goals into Google Ads, you can monitor your performance within Google Ads. Monitoring your data within Google Ads will allow you to analyze your campaigns’ profitability quickly, and you can quickly take actions based on the performance.
Besides conversion data, Google Ads provides significant metrics, all of which are important for determining your campaigns’ performance. Depending on the stage of your campaign, certain metrics are more relevant than others.
- Orientation
Impressions, CTRs, Clicks, on top rate, CPC, Quality Score, Clickout Rate - Optimization
Clicks, Conv. Rates, Conversions, Conv. Value, CPC, Cost, Quality Score, Clickout Rate - Scaling
Value / Cost, Conv. Value per Click, CPC
Now, a general metric setup we like to use is this one:
- Impr. (Abs. Top) %
- Impr. (Top) %
- CTR
- Clicks
- Clickout Rate
- Clickouts
- Conv. Rate
- Conversions
- Conv. Value
- Cost
- Profit & Loss
- Avg. CPC
- Cost / Clickout
- Cost / Conv.
- Conv. Value / Cost
- Quality Score (on levels where it is available)
This setup includes almost all the information we need to determine how the campaign is performing and which numbers could be improved.
4.1 How To Set Up Clickout, Clickout Rate And Profit & Loss Columns In Google Ads
Google Ads offers the capability to set up custom columns, which will help you better understand your performance. For example, you can easily set up affiliate link click-related metrics.
First of all, you will need to make sure you have integrated all your Google Analytics Goals you want to track within Google Ads under Settings & Billing > Conversions.
Make sure that your soft conversions, such as clickouts, are set to secondary conversion actions so that they do not mess with your conversion optimisation setup.
Once you have imported the relevant conversion goals from Google Analytics, you can set up the custom columns.
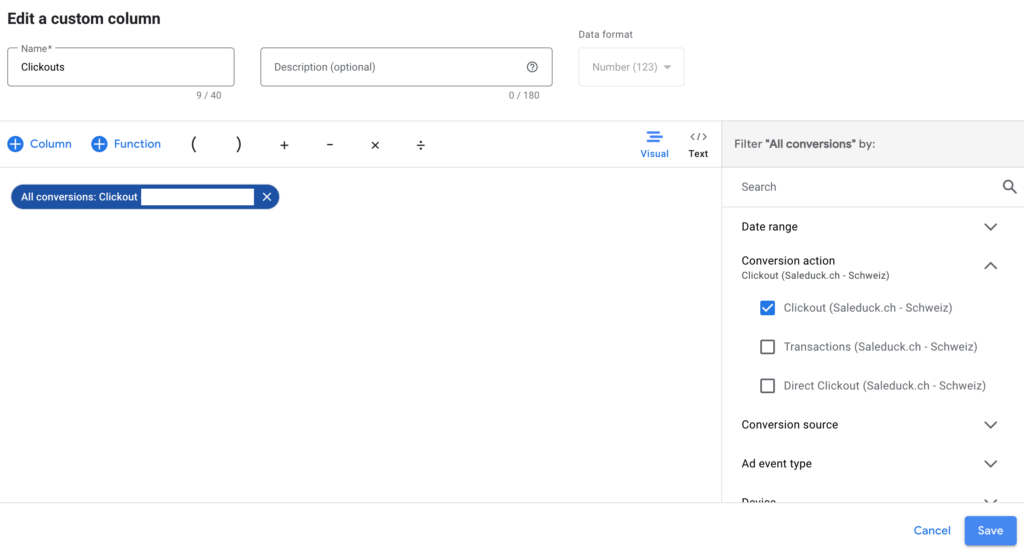
Clickouts:
- go back to your campaign overview
- click on Columns > Modify Columns
- Scroll all the way down and open the drop-down called ‘Custom columns’
- Click on ‘+ Custom Column’
- Type in ‘conversions’ and then select ‘all conversions’ from the dropdown
- Click on ‘Conversion action’, which appears on the right
- Tick the goal you would like to use (e.g., Clickout)
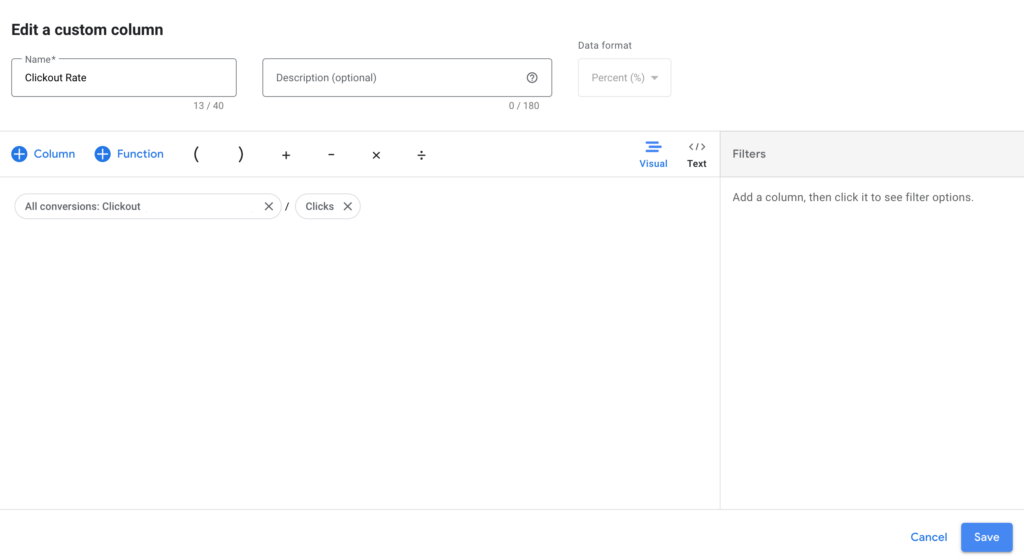
Clickout Rate:
Follow the same approach, but make sure to divide the clickout goal by clicks.
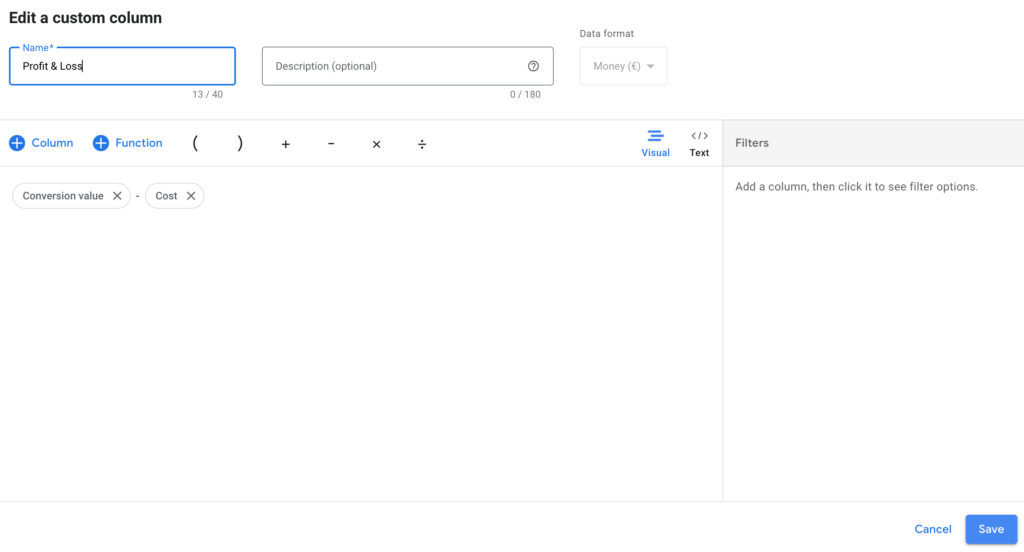
Profit & Loss:
Use Conv. value – Cost
Within Google Ads, you can also segment based on Conversion Actions. This will help you give a clear overview of which conversions your campaigns generated if you have multiple different ones integrated.
5. How To Optimize Google Ads (Affiliate) Campaigns Based On Performance
Once you have some campaigns running and generating impressions you can start optimising campaigns. We purposefully start with impressions here since these are the first numbers your campaigns will generate. Here we will dive into possible optimization and automation approaches based on the following metrics:
- Impressions
- Quality Score
- CTR & Clicks
- Clickout Rate & Clickouts
- Conversion Rate & Conversions
- Conversion Value & Cost
- CPC, CPA, Conv. Value per click & Conv. Value per Conversion
5.1 How To Optimize Your Google Ads Campaigns Based On Impression Data?
What is an impression in Google Ads?
The impression column gives you the number how often your ad was displayed.
Since there are different phases when it comes to Google Ads there are also different aspects that need to be considered. Let’s categorise the different phases as campaign start, campaign progress and campaign upscaling.
When you start a campaign, you need to make sure that it is generating impressions.
My campaigns do not generate any impressions, what can I do about that?
There are several reasons why your campaigns might not generate any impressions:
- Your bids are too low
- Temporarily increase bids to see if that helps
- Your ads are still under review
- Check the status of your ads, if it is under review then you will need to be patient.
- Your ads were disapproved
- Check the status of your ads, if it is disapproved then you will need to check whether your ads are violating Google Ads’ ad policies and adjust them accordingly.
- Your target audience is too small
- Check your audience settings and make sure it is big enough for Google to use it.
- Your keywords are not searched (might be too specific)
- Check the search volume of your keywords with Google Ads’ keyword planner. If their search volume is very low, make sure you include many alternative keywords or adjust the match type to either phrase or even broad match.
Now when your campaign has already been running for a while and you would like to increase its reach, there are some ways to increase the number of your impressions. Please consider that more impressions does not necessarily mean more clicks, conversions or revenue. If your campaigns generate irrelevant impressions, they can actually be harmful instead of beneficial, since they might affect your CTRs or generate irrelevant clicks which will drive your costs higher but not your conversions.
Nevertheless, here are some approaches of how to increase the number of impressions:
- Create new ads which are formulated differently and include alternative keywords in headlines and descriptions.
- Create ad groups containing your best performing keywords with broad match to collect data on search terms and get inspiration for new keywords.
- Increase your bids to be placed higher and more often. You need to consider that this will most likely increase the cost of your campaigns and might affect the profitability, so be careful with that approach.
When your campaigns have been running for a long time, generating many conversions and being profitable, you can make use of the collected data to improve your ad rankings for relevant users or to target relevant audiences with display ads.
- Place audiences in all your campaigns as observation audiences. E.g. ‘add users who clicked out’, ‘users who converted’ and ‘similar to users who converted’ and increase the bids for these. This will make sure that your ads will rank higher for users who are most relevant to your website.
- Create a display campaign that targets the audience ‘similar to users who converted’, this way you can target users who might not have interacted with your website yet but Google considers to be lookalikes from your converters.
5.2 How To Optimize Your Google Ads Campaigns Based On Quality Scores?
The Quality Score of your ads is very important to consider since it affects impressions and CPCs.
What is the Quality Score in Google Ads?
The quality score is a score from 1 to 10 determined by Google, expressing the relevance of your keywords.
What aspects are considered in the Quality Score of Google Ads?
Google Ads considers your landing page relevance, meaning whether the keywords you use are actually also being used on your landing page and within your ads. It also considers the experience on the landing page, for example whether the page is user and mobile friendly. Moreover, it considers the expected Click Through Rate, based on historic data and the afore mentioned characteristics.
How can I improve my Quality Scores?
In order to improve your Quality Scores you need to make your landing page and ads relevant to your keywords. This means, try to include the keywords you are using within your campaigns also in your landing page content and within your ad copies. Moreover, simply make sure that the ad and page content really delivers relevant information regarding the search keywords that are being used in your campaigns. Google always tries to make sure that the content they lead users too is relevant, meaning that it is helpful and really something the users are looking for.
How can I check my keyword Quality Scores?
In your keywords view click Columns > Modify Columns and search for the Quality Score metrics.
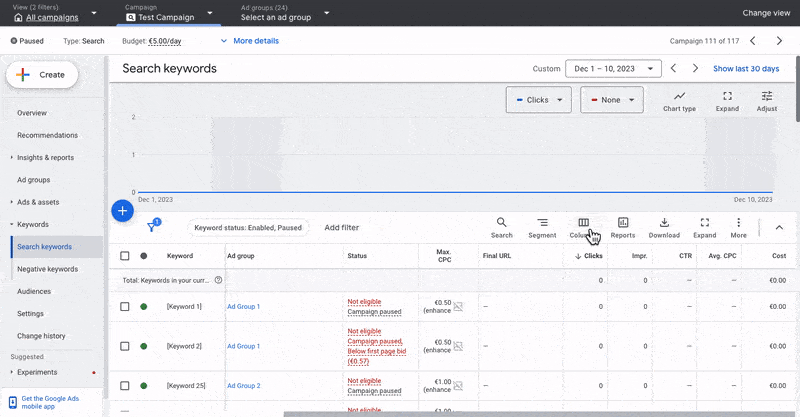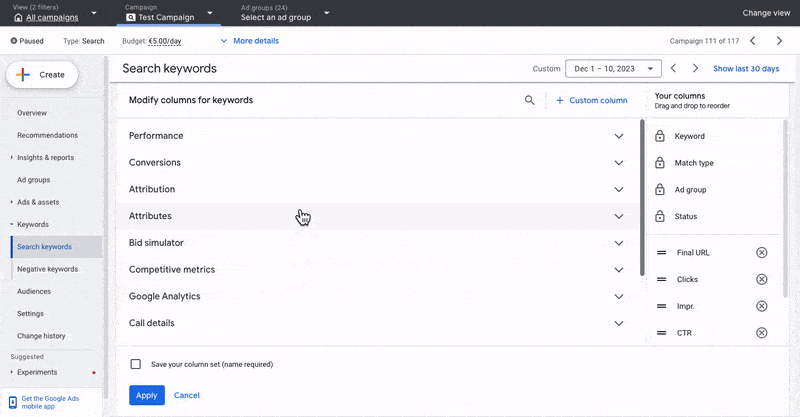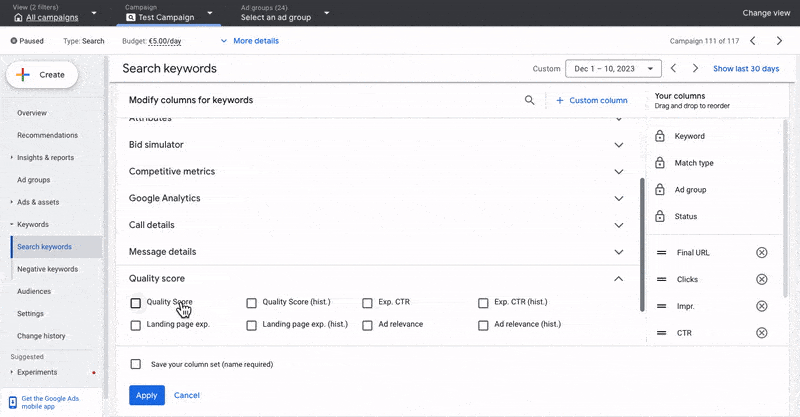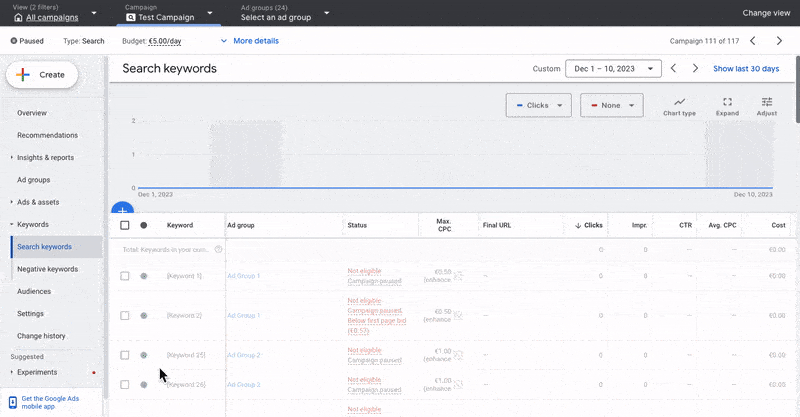
5.3 How To Optimize Your Google Ads Campaigns Based On CTR & Clicks?
While the number of impressions and the Quality Score has a significant impact on the CTR and, thus the number of Clicks, there are some practical tips you can consider to get your CTRs higher:
Ad Size
- Make use of ad extensions to make your ads bigger
Relevance
- Include campaigns’ keywords in ad headlines and ad description
- Make use of the keyword function in ad headlines and ad description
- Use Responsive Search Ads to let Google select relevant headlines and descriptions
Sense of Urgency
- Set a Countdown or Expiration date
- Promote limited discounts and coupons
Sense of Scarcity
- State a stock limitation
5.4 How To Optimize Your Google Ads Campaigns Based On Clickout Rates & Clickouts?
Next to optimizing your campaigns’ targeting, keywords, and ads, you need to optimize your landing page to generate conversions. The higher your Clickout Rate is, the more likely you will generate conversions. Here are some things you can consider to optimise your landing pages:
Relevant Content
The most important thing is that your content is relevant to your readers. Make sure that the pages you link to with your Google Ads campaigns are really relevant to the keywords you are using. Make your content easy to read, appealing to the reader’s eye (e.g., by using pictures), and delivering something that creates added value for your visitors.
User Experience
Ensure your readers can easily find the outgoing links and clarify that they will lead to the offer you are promoting. Do not try to make users click your links by baiting them; this might increase your Clickout Rates, but it might harm your overall conversion rates, and you might lose potential returning visitors.
In addition, see to it that your outgoing links work and lead to pages that are really relevant to your readers.
For example use affiliate deeplinks that directly lead to the products you are promoting so that your readers will not have to search for them on the merchants’ website.
(more coming soon…)
5.5 How To Optimize Your Google Ads Campaigns Based On Affiliate Conversions?
The most important metric is, of course, the conversion metric since that is the main goal you want to accomplish with your campaigns. To optimize conversions, you need to have your campaign running for some time to have enough data. You can then keep a close eye on which campaign elements drive conversions.
It is helpful to dive deep into the data, for example check which of your keywords are conversion drivers and be selective whether you want to continue to target keywords that do not drive any conversions since these might lower the profitability of your campaigns. Under Keywords > Search terms, you can actually check which search terms generate conversions for you. Based on that you can exclude certain search terms that do not drive any conversions to save these irrelevant costs.
You should analyze your conversion performance on every available level: ad group, ads, keywords, search terms, audiences, demographics, locations, ad schedule, etc. Doing so will allow you to better understand and optimize your campaigns.
If you notice that conversion rates significantly differ between your campaigns, it might very well be due to the content you are sending the traffic to. Properly analyse which of your pages convert well and try to replicate the page structure. To find out which page structure converts best, you can run A/B tests with tools such as Google Optimize (in the future via GA4).
You can then place links and content elements at different positions, switch out colours and other aspects of the page, and analyse which variant has better conversion rates.
5.6 How To Use 'Maximise Conversions' And Maximise Conversion Values' To Automate Google Ads Campaign Optimization Based On Affiliate Conversions?
The best and easiest way to optimize your Google Ads campaigns is to use Google’s machine learning and optimization capabilities. Google will then use your affiliate conversion data to optimize the targeting and bidding processes to reach people likely to convert. To use that functionality you need to have our affiliate conversion integration feature fully set up.
Once you are tracking affiliate conversions within your Google Ads account and some conversion data has been registered already, you can select ‘Maximise Conversions’ or ‘Maximise Conversion Value’ within the bidding section of your campaign settings.
When using ‘Maximise Conversions, ‘ you can set a target CPA to ensure that the price per conversion does not exceed your set limit on average. In order to calculate a good target CPA, you should look into your data and calculate the revenue you generate per conversion. If you then divide that value by 2 (or a smaller value above 1), it will be very likely that this campaign is set to be profitable.
When using ‘Maximise Conversion Value,’ you can set a target ROAS (return on ad spend). By setting that value above 100%, Google Ads will aim to make the campaign profitable, while set to 100%, it will merely aim to break even.
We recommend using the ‘Maximise Conversion Value’ bidding strategy when tracking is properly set up since Google Ads will have more flexibility to target the right users. In the long run, campaigns usually perform better then. If you are skeptical, you can, of course, A/B test different bidding strategies to see which one is the right fit for your campaigns (that’s what we usually do).